Vertical lathes
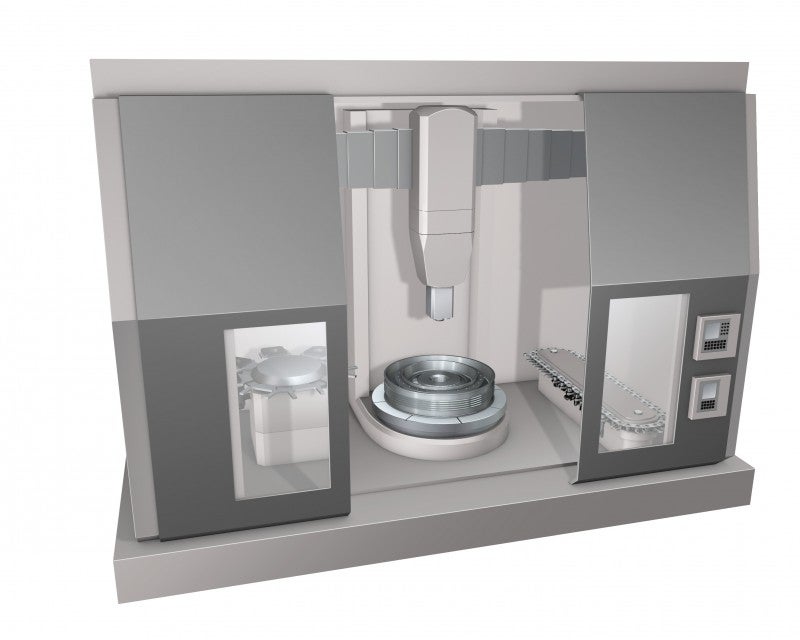

Vertical lathes, or VTL:s, are one of the most traditional machine types. They are ideal for heavy duty machining of medium to large parts. With different technologies, vertical lathes are also becoming more and more multifunctional.
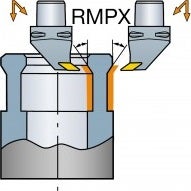
Vertical lathe machine configuration

Vertical lathes can machine components in diameter range from 1 meter to over 20 meters (39.37–787.40 inch). A gantry design with a RAM is the base of the construction.
Vertical lathes deliver very high metal cutting efficiency. However, the machine utilization can be a disadvantage due to tool change time and component loading, fixturing and unloading.
The need for large machines to machine concentric components has been revived over the last decade with the increase in energy and transportation demands. Gas, steam and wind turbines as well as aero engines all require large components with turning operations to be carried out. Railway wheel production has also seen a dramatic rise in quantities for freight as well as new inner city and high speed passenger lines.

Vertical lathe development
Development of new generation multifunctional machines is driven by several technologies.
Pre-measuring outside the machine to reduce set-up time, tool change time and measuring


- Quick change: Machines equipped with turning blocks can be equipped with manual quick change units. Providing change of tool holder in less than a minute with high accuracy and coolant internally directed. Thereby reducing the tool set-up and pre-measuring time compared to shank tools.
- Automatic tool change: From tool blocks with shank tool holders to hydro mechanical clamping units. Tools are automatically changed ensuring minimum downtime and allowing unmanned production.

Double RAMs

To increase metal cutting efficiency, two turning operations can be run simultaneously.
Rotating spindles
With the use of different attachments, held by four corner clamping or curvic couplings, a main spindle on the front centre of the RAM can provide drive to a 90 head. This enables a 4-axis machining centre, preventing the move of large components from a lathe to a machining centre which is both time and labour intensive.
Tool magazines
The need for space for more tools, due to more operations being carried out and more complex parts, is provided by chain magazines similar to large machining centres or multi-task machines rather than the traditional disc storage.

High pressure coolant

Piping the coolant through the RAM means there are no moving parts to provide sealing headaches (like rotating spindles and turrets). For extreme applications, a pressure up to 500 bar (7252 psi) is used in production on vertical lathes, however 70 bar (1015 psi) is the norm.
Automatic tool change with Coromant Capto®
A key to the versatility of a modern vertical lathes is its ability to accept many types of tool holder configurations on the end of the RAM. The attachments are changed automatically and stored in a separate rack. Automatic tool change ensures best machine utilization.

Coromant Capto® is the natural choice for turning operations and is also available for the rotating spindles with the same coupling size. This provides complete flexibility for tool storage. Depending on the component any combination of turning, milling, drilling and boring tools can be used with the same tool changer and magazine.
- C5, C6, C8, C10 are used for turning clamping units for manual quick change or hydro-mechanical automatic clamping. The orientation is flexible for axial or radial configurations and is often used for boring bars for internal diameters smaller than the RAM can access
- C8 and C10 are used when there are rotating spindles. With the same interface used for turning and rotating, there is complete flexibility for the mix of tools to be used
How to reach into smaller diameters than the RAM can access

The offset sleeve is designed for boring bar applications. It allows boring bars to reach into smaller diameters than the RAM can access.
C6 – minimum diameter: 103 mm (4.055 inch)
C8 – minimum diameter: 133 mm (5.236 inch)
C5 – minimum diameter: 76 mm (2.992 inch)
Use a right-hand or left-hand offset reduction adaptor to access a larger cutting unit program with the same RAM clearances.


Cutting units for profiling with axial clamping orientation are available.